Transforming Customer Experience with Conversational Banking
Conversational Banking has advanced from basic IVR systems to self-learning advanced AI-powered virtual assistants, driven by advancements in technology, customer preferences, and the need for more personalized and convenient banking experiences.
Initially, Interactive Voice Response (IVR) systems allowed customers to interact with automated phone systems using touch-tone keypads and predefined voice prompts. However, these systems had limited capabilities. Soon after it was introduced, natural language processing (NLP) paved the way for Text-Based Chatbots. Chatbots enabled customers to engage in text-based conversations with banking systems through websites or messaging apps. Early chatbots were rule-based and relied on predefined responses.

Virtual assistants like Siri, Google Assistant, and Amazon Alexa, propelled conversational banking further. These leveraged advances in natural language understanding (NLU) to interpret spoken queries. Voice Assistants provided a more natural and intuitive way to interact with banking services.
Banks began integrating conversational interfaces across various touchpoints, including mobile apps, websites, social media platforms, and messaging apps. This allowed customers to seamlessly switch between channels while maintaining continuity in their conversations. Omni-channel integration enabled a consistent and convenient banking experience across different platforms.
The latest evolution of conversational banking involves AI-powered Virtual Assistants specifically designed for the financial sector. These virtual assistants combine natural language processing, machine learning, and data analytics to provide personalized and context-aware banking services.
What is Conversational Banking?

Conversational banking leverages technologies like natural language processing (NLP) and artificial intelligence (AI) to understand customer queries, provide information, and perform banking tasks, all in a very human, natural feeling, conversational manner.
Conversational banking provides simplicity by way of enhanced customer experience, convenience, and accessibility. Customers can communicate with the banking system through their preferred messaging platforms or voice assistants, making the interaction more intuitive and user-friendly.
Conversational banking can also be integrated into various touchpoints, such as mobile apps, websites, social media platforms, or smart devices, making banking services available wherever customers are.
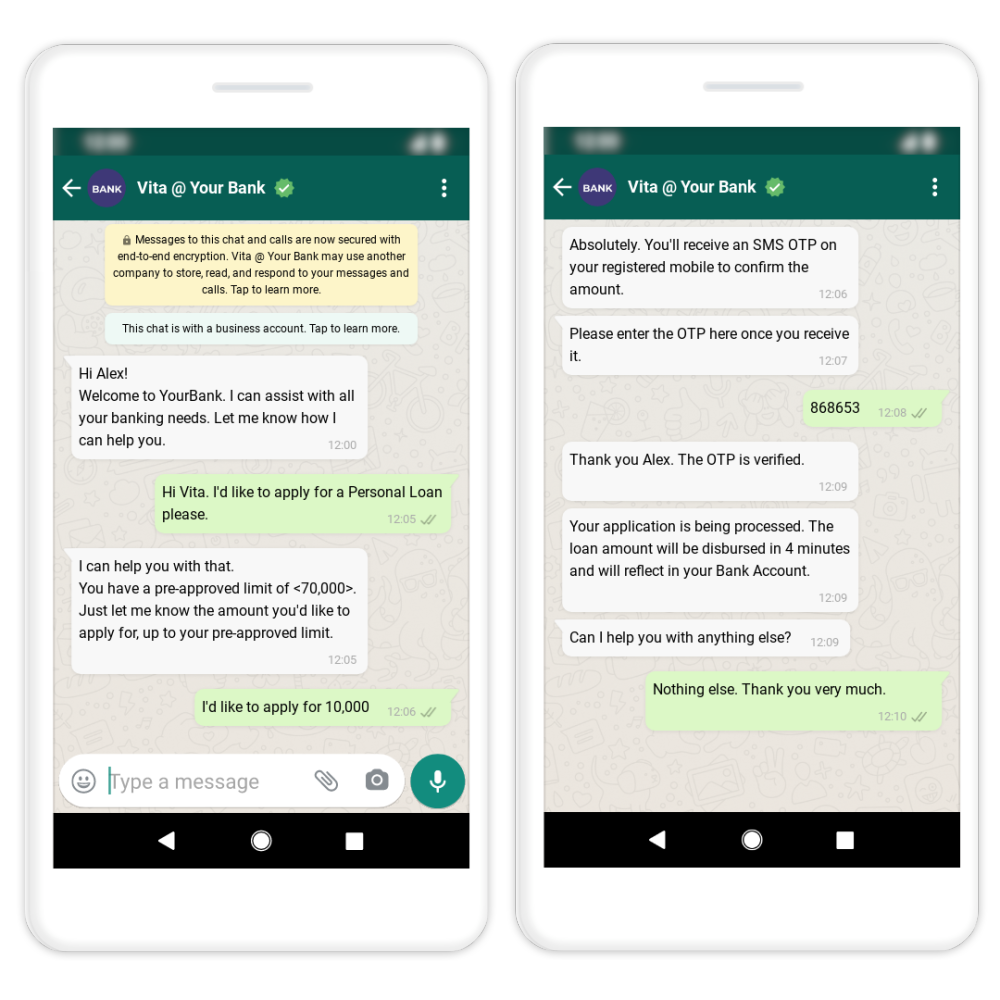
Benefits of Conversational Banking for BFSI

Conversational banking offers several key benefits for financial establishments. Implementing conversational banking solutions can lead to significant cost savings for financial establishments. By automating routine inquiries and transactions through chatbots or virtual assistants, financial institutions can reduce the need for human customer support interventions. The technology can also handle a large volume of customer interactions simultaneously, increasing efficiency. Scalability and efficiency improve overall operational productivity and ensure prompt customer service.
Conversational banking extends service availability of banking services beyond traditional working hours and physical branch locations. Customers can access services anytime and anywhere through their preferred messaging platforms or voice assistants.
The technology can improve Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) by enhancing customer satisfaction, engagement, and loyalty. By providing personalized and convenient interactions, conversational banking strengthens customer relationships, leading to longer customer retention. The seamless and efficient customer support offered by chatbots and virtual assistants can improve problem resolution and can reduce churn.
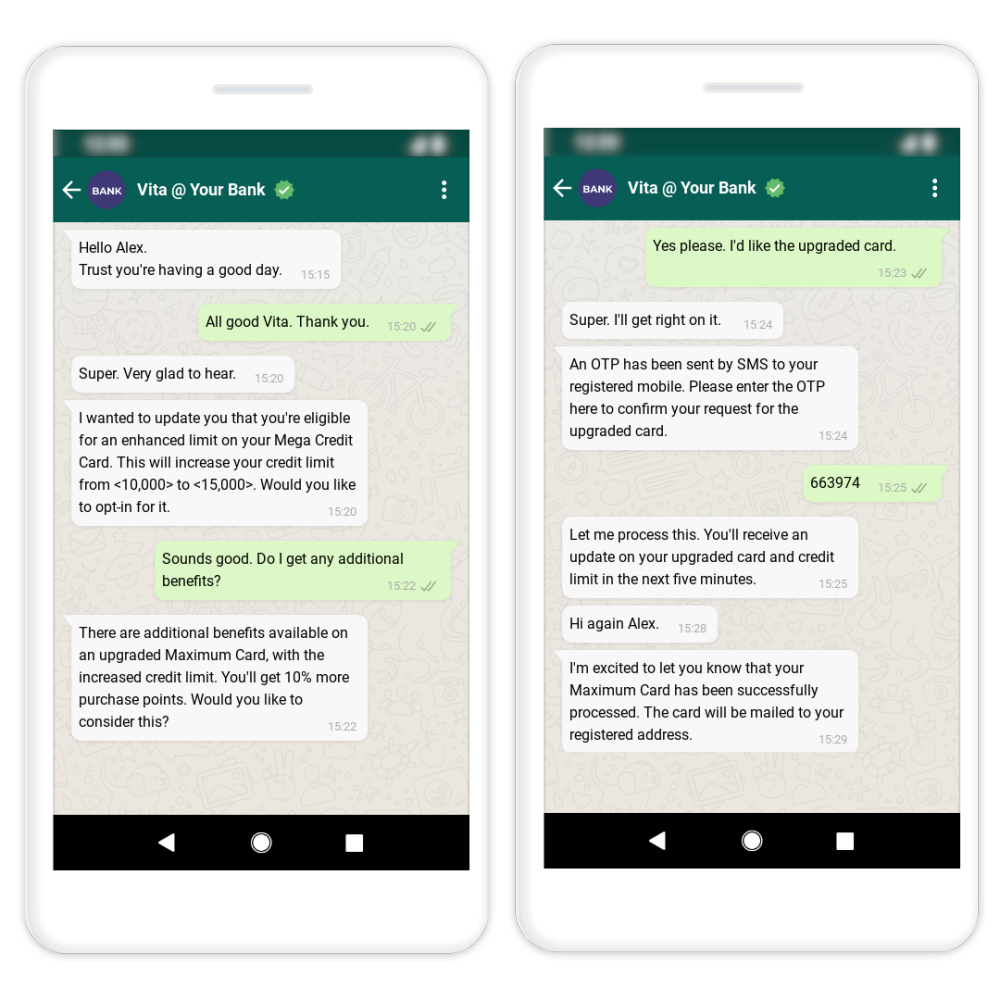
Conversational banking allows financial institutions to provide instant innovative and efficient customer support. Chatbots and virtual assistants can handle a wide range of customer inquiries, resolving issues quickly and accurately. By addressing customer needs promptly and effectively, financial institutions can improve customer satisfaction. Satisfied customers are more likely to continue using the institution’s products and services, thereby driving revenue growth.
Conversational banking solutions can be designed to ensure compliance with regulatory requirements and data security standards. Financial establishments can implement measures such as encryption, secure authentication, and data privacy safeguards to protect customer information and maintain regulatory compliance. This instills trust and confidence in customers.
The Transformative Role of AI Chatbots in Banking

Let’s explore the significant role of conversational AI in banking and its impact on customer experience, operational efficiency, and overall industry transformation.
Chatbots and virtual assistants can handle a wide range of routine inquiries and transactions. Conversational AI systems can guide customers through complex processes such as account opening, loan applications, or dispute resolutions, ensuring efficient and effective support.
By analysing customer profiles, transaction histories, and preferences, AI-powered systems can provide tailored recommendations, offers, and advice. For example, a virtual assistant can suggest suitable financial products based on a customer’s financial goals and spending patterns.
Chatbots and virtual assistants can handle a large volume of customer interactions simultaneously, reducing the need for human agents to handle routine inquiries. This automation at scale improves operational efficiency and reduces costs.
Conversational AI has become a cornerstone of digital transformation in the banking industry. Its ability to deliver personalized experiences, streamline customer interactions, and improve operational efficiency makes it a powerful tool for financial institutions. With conversational AI, banks can enhance customer experience, provide efficient support, and gain valuable insights for continuous improvement.
Uses for AI-enabled systems in the Banking Industry
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has numerous use cases and examples in the banking industry. Some of the most some prominent ones are:
Fraud Detection and Prevention
AI-powered systems can analyse vast amounts of data, including transaction records, customer behaviour patterns, and historical fraud cases, to detect and prevent fraudulent activities in real-time.
Customer Service and Support
Chatbots and virtual assistants driven by AI can provide personalized customer support, answer inquiries, and assist with routine banking tasks. Conversational AI agents can understand natural language, offer real-time responses, and guide customers through various processes.
Intuitive, AI-enabled automation could also be provided for customer banking needs such as:
- New account opening
- Balances inquiry
- Money transfers
- Third-party billing and payments through integrations
- Account management (E.g. password changes, address changes, etc)
- Personalised offer processing
- Automated upsell processing
- Credit card and loan pre-evaluations
Risk Assessment and Credit Scoring
AI algorithms can analyse customer data, credit histories, and other relevant factors to assess creditworthiness and determine risk profiles. AI-powered credit scoring models can make more accurate and data-driven credit decisions.
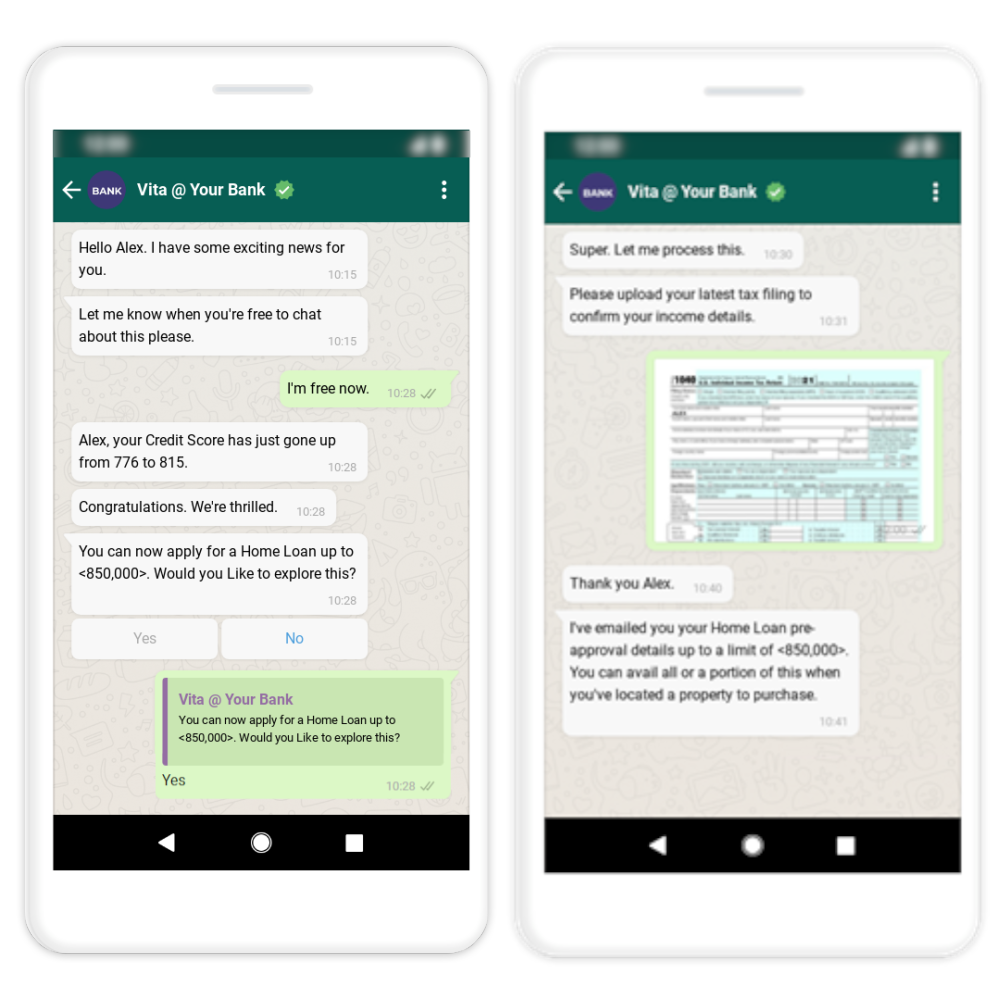
Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
RPA utilizes AI and automation technologies to automate repetitive and rule-based tasks within banking processes. It can automate data entry, account reconciliation, compliance checks, and other back-office operations.
Personalized Recommendations and Upselling
AI algorithms can minutely analyse customer data, transaction history, and behaviour patterns automatically. By leveraging machine learning techniques, banks can present customers with tailored suggestions for investment options, insurance policies, or other financial products.
Sentiment Analysis and Customer Insights
AI-powered sentiment analysis techniques can analyse customer feedback, social media conversations, and customer interactions to gain insights into customer sentiment, preferences, and satisfaction levels. By understanding customer sentiments, banks can identify emerging trends, improve products and services, and proactively address customer concerns.
How to successfully implement a conversational banking experience
Understanding customers’ needs is crucial before implementing conversational banking. Conducting customer research and surveys, engaging in social listening, collaborating with frontline employees and gathering feedback from a small group of customers, can help fine-tune the conversational banking solution.
Designing customer journeys is a critical step before implementing conversational banking. Start by mapping out the different touchpoints and interactions customers have with the bank. Identify key customer personas and their specific needs and pain points at each stage of the journey. Use customer data and feedback to understand their preferences and expectations. Consider integrating conversational banking at the appropriate touchpoints.
Designing effective customer support and engagement systems is crucial before implementing conversational banking. Determine the appropriate channels for support, such as chatbots, virtual assistants, or a combination. Define clear escalation paths for complex issues that require human intervention. Develop a knowledge base and train the AI system to provide accurate and relevant responses. Implement sentiment analysis to gauge customer satisfaction and adjust the system accordingly.
Summary

Looking ahead, the seamless integration of conversational banking across multiple channels and devices will become the norm. Customers will expect consistent and personalized experiences across various touchpoints, including mobile apps, websites, messaging platforms, and voice assistants. Banks will need to ensure a cohesive and frictionless experience throughout the customer journey.
Related Media
8 ways to enhance your customer experience
When a customer engages with your company, whether it’s to obtain a service or buy a product or solution, one basic expectation underpins the engagement— receiving a great experience.
The changing digital communications landscape has created a need for cloud communications and platform-based customer engagement models
With an increasing fragmentation of communications channels, along with fragmentation in consumer preferences, organisations need to be able to find ways to communicate and engage with their customers across multiple forms of media.
TATA COMMUNICATIONS DIGO programmable voice communication
Organizations worldwide are adopting a cloud communications approach, also known as Communications Platform as a Service (CPaaS).
